Handbags are more than accessories—they’re icons of style, commerce, and craftsmanship. From luxury runways to street markets, the handbag industry drives innovation and generates billions in revenue worldwide. In 2023, global handbag sales topped $60 billion, and by 2030 they’re projected to reach $81.79 billion at a 6.5% CAGR, underscoring the sector’s explosive growth and cultural impact.
Handbags manufacturing combines creative design, meticulous material selection, precision cutting, skilled assembly, rigorous quality control, and thoughtful packaging to transform raw hides and fabrics into finished products ready for market. This multifaceted process merges artisanal techniques with advanced technology to meet evolving consumer demands.
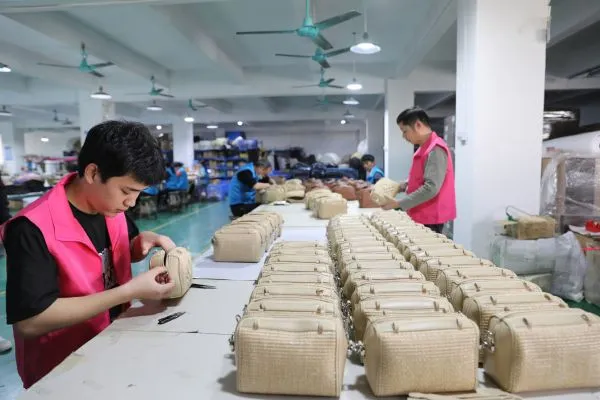

The journey begins with designers sketching concepts inspired by fashion trends and consumer insights. Next comes prototyping and tech‑pack development, followed by sourcing premium leathers, synthetics, and eco‑friendly alternatives. Skilled artisans then prepare and cut materials—often using CNC machines for consistency—before assembling components through expert stitching and hardware installation. After multi‑stage inspections ensure durability and compliance with ISO and environmental standards, each handbag receives final touches like edge painting, embossing, and protective packaging.
Imagine a small atelier in Cambodia that once struggled to scale its handcrafted satchel line. After adopting streamlined production workflows and investing in CNC cutting and ISO‑certified QC, they tripled output while maintaining artisanal quality—proving that understanding every manufacturing step isn’t just academic, but the key to turning artisan dreams into global brands.
Design and Prototyping
Quick Answer: In the design and prototyping phase, ideas become physical samples through creative concept work, detailed tech packs, iterative sampling, and close collaboration—ensuring your handbag’s look, function, and brand identity perfectly align before production.
Conceptual Design
Conceptual design sets the creative foundation for every handbag. Designers immerse themselves in current trends, consumer insights, and brand DNA to sketch silhouettes that resonate. This phase transforms abstract ideas into tangible visuals that guide the entire production process.
- Trend Research: Analyze runway shows, social media (Instagram, TikTok), and street style.
- Mood Boards: Combine color palettes, textures, and hardware inspirations.
- Sketch Iterations: Rapid hand or digital sketches to refine silhouettes.
- Consumer Input: Incorporate feedback from target demographics and focus groups.
Creating a Technical Specification (Tech Pack)
A tech pack is the production blueprint that bridges design and manufacturing. It converts sketches into precise instructions for cutting, stitching, and assembly, reducing costly errors. Clear tech packs accelerate sampling and ensure consistency across production runs.
- Detailed Dimensions: Exact height, width, depth, and strap lengths.
- Material Call‑Outs: Specify hide thickness, grain direction, fabric weights.
- Stitch & Seam Instructions: Define stitch type, spacing, and reinforcement points.
- Hardware Placement: Pinpoint zipper types, buckle sizes, and logo positions.
Prototype Development
Prototyping turns tech packs into physical samples, revealing design strengths and weaknesses. Skilled pattern makers draft precise templates, then artisans cut and assemble test materials. Each prototype undergoes evaluation to fine‑tune fit, function, and finishing details.
- Pattern Making: Draft paper or CAD patterns for each panel.
- Sample Cuts: Use stock materials (leather or mock‑up fabrics) for initial builds.
- Fit & Function Tests: Evaluate strap comfort, pocket access, and closure ease.
- Iteration Rounds: Refine based on wear tests and designer feedback (2–4 cycles).
Customization & Collaboration with Designers
Successful prototypes lead to close collaboration between brands and manufacturers. At this stage, bespoke elements—hardware, materials, branding—are finalized. Open communication and rapid feedback loops ensure the final sample meets both aesthetic and technical requirements.
- Bespoke Hardware: Custom metal finishes, engraved clasps, unique zipper pulls.
- Material Swaps: Eco‑friendly leathers, recycled fabrics, vegan alternatives.
- Brand Details: Embossed logos, signature linings, personalized hangtags.
- Rapid Feedback Loops: 3D renders and small‑batch prototyping to lock design choices fast.
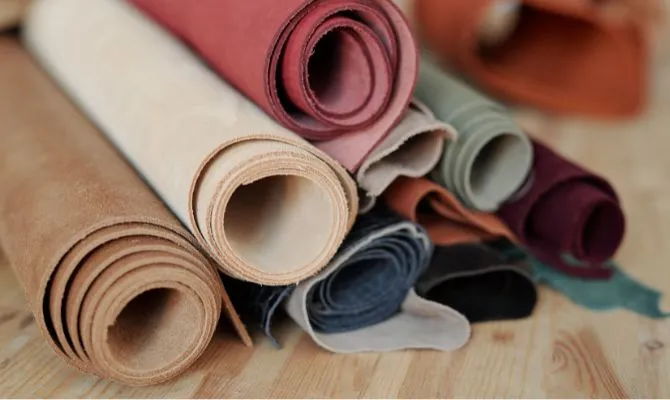
Types of Materials: Leather, Synthetics, Eco‑Friendly
Full‑Grain Leather
Full‑grain leather features the intact natural hide surface, prized for its durability and ability to develop a rich patina over time. It retains original grain markings and strength, making it the top choice for premium satchels, structured totes, and investment‑level clutches that age beautifully with use.
- Highest tensile strength and tear resistance
- Natural markings unique to each hide
- Ideal for luxury and heirloom pieces
Top‑Grain Leather
Top‑grain leather undergoes light sanding to remove surface imperfections, offering a more uniform finish at a slightly lower price point. It balances aesthetics and durability, making it well‑suited for everyday hobo bags, backpacks, and briefcases that benefit from a refined appearance without the premium cost of full‑grain.
- Sanded for consistent color and texture
- Moderate patina development over time
- Used in high‑volume, mid‑market styles
PU & PVC Synthetics
Polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) leathers mimic animal hides at a fraction of the cost. These water‑resistant materials are lightweight, easy to clean, and available in endless colors and finishes. They’re popular for budget‑friendly crossbody bags, gym duffles, and children’s backpacks that require durability and simple maintenance.
- Highly water‑repellent and stain‑resistant
- Wide range of textures and colors
- Cost‑effective for mass production
Nylon
Nylon is a high‑strength synthetic fabric known for its exceptional durability and light weight. Often used in backpacks, travel totes, and technical messenger bags, nylon resists abrasion and moisture, making it ideal for active lifestyles. Its quick‑dry properties and easy cleaning make it a practical choice for everyday commuters and adventurers.
- Superior tensile strength and tear resistance
- Water‑repellent coatings available
- Easy to wash and fast‑dry
Canvas
Canvas is a woven cotton or cotton‑blend fabric celebrated for its rugged texture and casual appeal. Used in shopper totes, beach bags, and eco‑friendly market purses, canvas offers substantial capacity and structure. It can be treated for water resistance and printed with vibrant designs, making it a versatile, sustainable choice for both functional and fashion‑forward bags.
- Thick, durable weave withstands daily wear
- Custom prints and dye options
- Often machine‑washable for easy care
Neoprene
Neoprene is a stretchable synthetic rubber fabric prized for its shock‑absorbent and insulating properties. Common in lunch box bags, sporty backpacks, and casual clutches, neoprene offers cushioning and shape retention. Its unique texture and modern aesthetic appeal to active and urban consumers seeking lightweight, protective carry solutions.
- Excellent abrasion and tear resistance
- Flexible, protective cushioning
- Resistant to water and temperature changes
Recycled PET
Recycled PET fabrics are woven from post‑consumer plastic bottles, transforming waste into durable, lightweight textiles. Used in eco‑friendly shopper bags, weekend totes, and casual backpacks, PET blends offer water resistance and easy maintenance. Their sustainable origin helps brands meet green credentials without sacrificing performance or style.
- Reduces plastic waste in landfills
- Comparable durability to virgin polyester
- OEKO‑TEX or GRS certified options
Plant‑Based Leather
Plant‑based leathers use agricultural byproducts—cactus, pineapple leaf fiber, or apple peels—processed into supple, eco‑friendly hides. These materials appeal to vegan and sustainable markets, offering a leather‑like feel for casual totes, clutches, and fashion accessories. As technology advances, their durability and finish approach traditional leather standards.
- Biodegradable and renewable resources
- Growing color and texture variety
- Suitable for conscious fashion lines
Cork
Cork leather is harvested from tree bark, creating a lightweight, water‑resistant, and hypoallergenic material. Its natural texture and sustainable sourcing make it popular for statement handbags, wallets, and eco‑chic crossbodies. Cork’s durability and unique grain patterns offer an artisanal look that resonates with environmentally conscious consumers.
- Renewable bark harvesting process
- Natural water repellency
- Distinctive organic patterns
Mass Production & Scaling
Transition from Prototypes to Production Runs
Once prototypes are approved, manufacturers shift to full production by refining processes and securing raw materials at scale. This phase involves setting target batch sizes, establishing cost analyses, and scheduling pilot runs. Clear communication between design and production teams ensures that any last-minute adjustments are captured. By aligning technical specs with manufacturing capabilities, brands can avoid costly rework and meet delivery timelines without compromising the craftsmanship that defined the prototypes.
- Define batch volumes and pricing tiers
- Conduct pilot runs to validate production workflows
- Finalize material procurement schedules
- Coordinate design changes with factory engineers
- Set up initial quality checkpoints
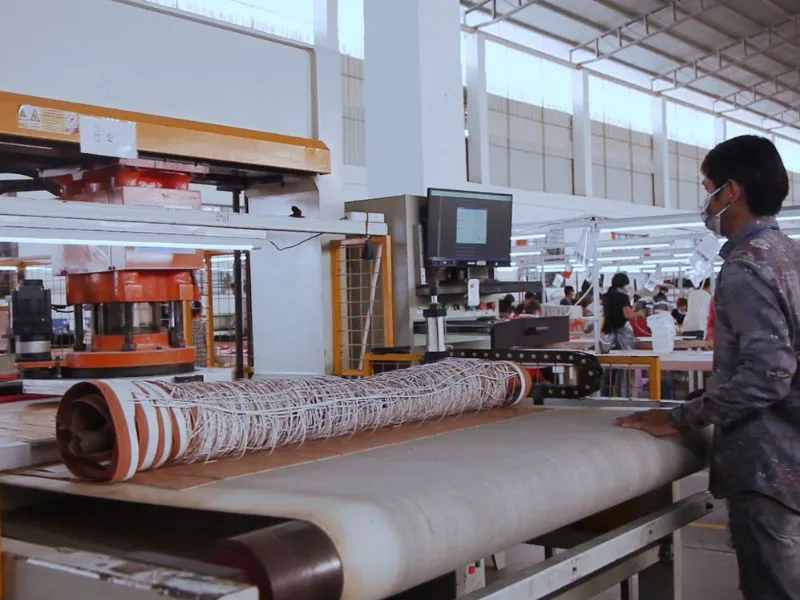
Production Line Setup & Workflow Optimization
Efficient production lines maximize output and minimize waste. Factories design floor layouts to streamline material flow—from leather storage to cutting tables, stitching stations, and final assembly. Lean manufacturing principles, such as 5S and Kaizen, are applied to eliminate bottlenecks. Cross‑training workers on multiple tasks ensures flexibility during peak demand. Real‑time dashboards monitor throughput, enabling managers to adjust staffing and machine usage dynamically, keeping lead times predictable and quality consistently high.
- Map material and work-in-progress flow
- Implement 5S organization at each station
- Use time-motion studies to set takt times
- Cross-train operators for multi‑skill coverage
- Monitor KPIs via digital production dashboards
Material Preparation
Material preparation readies all components for assembly. Pattern cutting uses a mix of manual dies and CNC machines for precision and speed. Leathers and fabrics undergo conditioning to remove wrinkles, improve pliability, and apply protective coatings. Linings, interfacing, and hardware—zippers, buckles, eyelets—are sorted and pre‑assembled in kits. This pre‑kitting approach accelerates downstream processes and guarantees that every bundle entering the line contains the correct parts for each handbag style.
- Pattern Cutting: Manual dies for small batches; CNC for high volumes
- Treatment: Leather softening, fabric waterproofing, UV‑resistant finishes
- Component Kits: Pre‑cut linings, straps, zipper pulls, and clasps
- Labeling: Tag materials with SKU and lot numbers for traceability
Assembly Process
Assembling handbags combines machine precision with artisan skill. Stitching techniques vary: straight stitches for seams, zigzag for stretch areas, and overlock to finish raw edges. Hardware installation—riveting buckles, attaching straps, setting eyelets—is done with pneumatic tools or hand presses. Panels are joined and reinforced to form the bag’s skeleton before attaching external layers and linings. Luxury lines may include hand‑finished edges, while volume brands rely on automated machines for consistent stitch quality.
- Straight, zigzag, and overlock stitching with single‑ and multi‑needle machines
- Pneumatic presses for rivets, grommets, and hardware
- Frame and gusset construction to define shape
- Hand‑edge painting vs. machine‑applied edge sealants
- Balancing handcrafted finishes with automated consistency
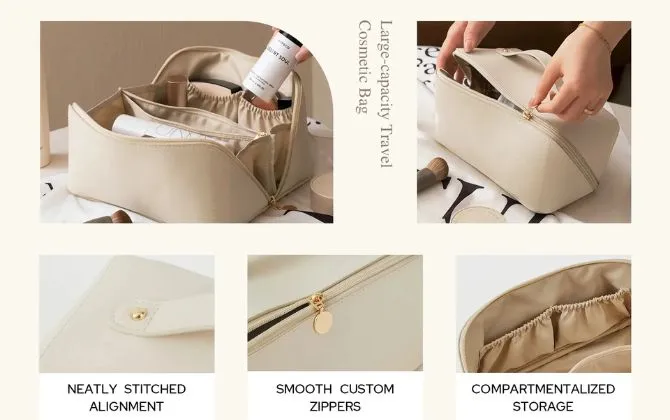
Quality Control
Quality control safeguards each production batch. Incoming inspections verify hide thickness, color uniformity, and tensile strength. Inline checks monitor stitch tension, alignment, and hardware placement during assembly. Final audits assess overall appearance, functionality, and durability—zippers must glide smoothly, seams must withstand load tests, and finishes must resist scuffing. Compliance with ISO9001 and environmental standards ensures ethical practices and product safety, giving brands confidence in their supply chain integrity.
- Incoming: Material certification, defect scanning, moisture content tests
- Inline: Stitch audits, zipper pull tests, dimensional checks
- Final: Double‑rub abrasion, weight load, drop and stress testing
- Compliance: ISO9001, LWG, REACH, and SMETA audits
Finishing Touches
The final steps add polish and brand identity. Handbags are cleaned with soft brushes and polished to remove dust or dye residues. Logos are embossed, heat‑pressed, or metal‑plated onto hardware. Tags and swing charms are attached according to brand guidelines. Finally, each bag is carefully packaged—wrapped in tissue, enclosed in dust bags, and boxed with silica packs and care instructions—ready for shipment under optimal protective standards.
- Cleaning & Polishing: Soft cloths, gentle solvents, leather conditioners
- Branding: Embossing presses, heat transfers, custom metal logos
- Packaging: Dust bags, branded boxes, silica gel inserts, wrap‑and‑seal protocols
- Shipping Prep: Barcode labeling, carton grouping by SKU, palletizing
Packaging & Shipping
Packing
Packing transforms finished handbags into protected, shipment‑ready units. Each order follows a detailed packing list, specifying carton counts, units per carton, and protective bag quantities. Handbags are first placed in compostable poly bags to guard against moisture, odors, and scuffs. These eco‑friendly liners break down in home compost systems, eliminating plastic waste. Once bagged, units are organized into standardized cartons—designed to optimize space and prevent shifting—before labeling and sealing for transit.
- Compostable inner bags protect against dampness and odors
- Packing lists detail units per protective bag and carton
- Standardized carton sizes maximize space utilization
- Cartons are sealed, labeled, and cross‑checked against order specs
- Eco‑friendly materials replace traditional plastic wraps
Shipping
Shipping logistics balance cost, speed, and environmental impact. For orders over 500 units, sea freight offers a cost‑effective, lower‑carbon option, with transit times of 5–6 weeks. Air freight is available for urgent smaller shipments, delivering within 7–10 days. Hoplok coordinates container dispatch every two weeks, consolidating orders to optimize load efficiency. Upon arrival, cartons undergo customs clearance, quality checks, and are transferred to local warehouses for final domestic delivery or staged release per client requirements.
- Sea freight for large orders: 5–6 week transit, lower emissions
- Air freight for urgent shipments: 7–10 day delivery
- Bi‑weekly container departures ensure timely dispatch
- Customs clearance and quality checks upon arrival
- Flexible warehousing and staged delivery available
Technology in Handbag Manufacturing
Automation & Machinery
Modern handbag factories leverage automated equipment to boost precision and throughput. CNC leather cutters slice panels with micrometer accuracy, reducing material waste by up to 15%. Robotic sewing stations handle repetitive stitch patterns—straight, zigzag, and overlock—at speeds exceeding 2,000 stitches per minute. Pneumatic presses affix hardware like rivets and grommets uniformly, while automated edge‐painting machines apply sealants consistently. Together, these machines free artisans to focus on quality‑critical tasks and complex hand finishes.
- CNC cutting tables for consistent panel shapes and minimal scrap
- Automated multi‑needle sewing machines for high‑speed stitching
- Pneumatic presses to install rivets, eyelets, and buckles
- Edge‑painting robots for uniform sealant application
Design & Production Planning Software
Digital tools streamline the transition from concept to factory floor. CAD software enables precise pattern drafting, grading, and 3D visualization, ensuring fit and proportions before any material is cut. PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) systems consolidate tech packs, bill of materials, and revision histories in a single platform—reducing errors and shortening time‑to‑market by up to 30%. Real‑time dashboards track sample approvals, material lead times, and production milestones, allowing teams to anticipate bottlenecks and adjust workflows proactively.
- CAD for pattern creation, nesting, and 3D sampling
- PLM for centralized tech packs, BOMs, and version control
- ERP integration to synchronize inventory and production schedules
- Dashboard KPIs for on‑time delivery and quality metrics
Innovative Technologies
Emerging tech transforms handbag functionality and personalization. 3D printing produces custom hardware prototypes—buckles, clasps, and logos—accelerating design approval cycles. RFID‑blocking linings embedded during lining assembly protect credit cards and passports from skimming. AI‑driven cutting optimization analyzes hide topography to maximize yield. Blockchain traceability solutions can log each material’s origin and processing history, offering consumers transparent supply‑chain credentials and bolstering brand trust in an era of ethical sourcing.
- 3D printed hardware prototypes for rapid iteration
- RFID‑blocking fabrics integrated into linings
- AI algorithms for nesting patterns and reducing waste
- Blockchain tracking for material provenance and transparency
Sustainability in Handbag Production
Eco‑Friendly Materials & Practices
Integrating eco‑friendly materials reduces environmental impact and appeals to conscious consumers. Manufacturers use recycled PET fabrics, plant‑based leathers (pineapple, cactus), and LWG‑certified hides. Compostable inner bags and water‑based dyes further minimize toxicity. These practices balance performance with green credentials and brand values.
- Recycled PET and upcycled fabric blends
- Plant‑based leathers from pineapple or cactus fibers
- LWG‑certified full‑grain and top‑grain hides
- Water‑based, low‑VOC dye processes
- Compostable or biodegradable inner packaging
Reducing Waste & Energy Consumption
Efficient resource use drives cost savings and sustainability. Advanced nesting algorithms maximize material yield, cutting scrap by up to 20%. Factories implement water recycling systems, LED lighting, and solar panels to lower utility demands. Lean manufacturing and circular production models ensure minimal waste throughout the supply chain.
- AI‑driven pattern nesting to reduce fabric offcuts
- Leather trimming repurposed for smaller goods or accessories
- Water recycling in tanning and dyeing processes
- LED lighting and solar energy integration
- Circular economy models for material reclamation
Ethical Labor Practices
Fair labor practices are essential for sustainable production. Manufacturers adhere to SMETA and BSCI standards, ensuring safe work environments and fair wages. Regular third‑party audits verify compliance. Training programs and career development initiatives empower workers, fostering long‑term relationships and maintaining high craftsmanship standards.
- SMETA and BSCI certification for ethical compliance
- Fair wages aligned with local living standards
- Safe working environments and ergonomic stations
- Regular third‑party social audits
- Skills training and career development programs
Challenges and Future Trends in Handbag Manufacturing
Handbag manufacturing faces rising material costs, counterfeit competition, and shifting consumer demands. At the same time, personalization, smart features, and sustainable practices are reshaping design and production, driven by technological advances and evolving shopper preferences.
Common Manufacturing Challenges
Manufacturers contend with volatile raw material prices—leather and metal hardware can fluctuate 10–20% annually—impacting margins. Counterfeit goods dilute brand value and patient design investments. Additionally, complex global supply chains introduce lead‑time uncertainties, requiring robust contingency planning to avoid production delays.
- Leather price volatility and metal tariff fluctuations
- Proliferation of low‑quality counterfeits undermining brand integrity
- Supply chain disruptions and extended lead times
- Rising labor and compliance costs in multiple regions
Emerging Trends in Design & Production
Personalization is booming—on‑demand embossing, color selection, and modular hardware let consumers co‑create. Smart bags integrate tech like wireless charging and GPS tracking. Hybrid production models mix small‑batch artisanal runs with automated volume phases, giving brands agility and exclusivity in equal measure.
- Custom embossing, monogramming, and color‑on‑demand services
- Smart features: RFID pockets, wireless charging panels, GPS modules
- Micro‑runs powered by agile manufacturing for limited editions
- Blended artisan and automated workflows for flexibility
Impact of Technology & Consumer Preferences
Advances in AI and blockchain drive transparent sourcing and waste reduction, appealing to eco‑conscious buyers. Growing demand for vegan and recycled materials pushes innovation in plant‑based leathers. Social media trends shorten product life cycles, requiring faster sampling and production turnaround to stay relevant.
- AI for demand forecasting, reducing overproduction
- Blockchain for verifiable ethical sourcing and traceability
- Surge in plant‑based and recycled material adoption
- Accelerated timelines from viral trends to retail shelves
Hoplok Can Help You Develop Your Own Handbag Product Line
Partnering with a Trusted Manufacturer
Hoplok Leather combines 22+ years of expertise with ISO9001 and SMETA certification to deliver reliable, on‑time handbag production. Our dual‑facility setup in Cambodia and China ensures regional flexibility and consistent quality across diverse product lines.
- Three factories with 50,000㎡ capacity and 1.2 million monthly units
- American‑trained designers liaise directly with production teams
- 24/7 customer support and dedicated project managers
- Compliance with global standards (ISO9001, BSCI, LWG)
Customization & Scalability
From limited‑edition prototypes to large production runs, Hoplok adapts to your needs. We offer flexible MOQs starting at 100 units, rapid 2–7 day sampling, and scalable manufacturing up to tens of thousands of pieces per month, all with factory‑direct pricing.
- Flexible MOQs—from 100 to 50,000 units
- Rapid prototyping: 2–7 day sample turnaround
- Material sourcing across Italy, Pakistan, Argentina, Brazil
- Tiered pricing to optimize budgets and margins
Streamlined Production Process
Our integrated in‑house workflow—from design consultation to final packaging—ensures seamless communication and quality control at every stage. Real‑time production dashboards, multi‑stage inspections, and lean practices minimize delays and defects for efficient, high‑quality output.
- End‑to‑end turnkey solutions: concept to delivery
- CNC cutting, automated sewing, and rigorous QC audits
- Lean manufacturing with 5S and Kaizen principles
- Transparent reporting via digital production dashboards
Why Choose Hoplok as Your Handbag Manufacturing Partner?
Hoplok Leather stands out with its blend of artisanal craftsmanship and technological innovation. Our commitment to sustainability, competitive factory pricing, and global logistics support makes us the ideal partner for brands seeking quality, flexibility, and growth in the handbag market.
- Certified ethical practices and eco‑friendly options
- Factory‑direct pricing to maximize your ROI
- Global shipping and after‑sales logistics support
- Proven track record with over 1,500 international clients
Conclusion
Handbag manufacturing is a complex journey—from initial concept and material selection through mass production, quality control, and finishing touches. Each step blends artisanal skill with advanced technology, ensuring that every tote, clutch, and satchel meets exacting standards.
Innovation and sustainability are no longer optional. Embracing eco‑friendly materials, automation, and transparent supply chains not only reduces environmental impact but also resonates with today’s conscious consumers.
Ready to bring your own handbag vision to life? Partner with Hoplok Leather for turnkey design, customizable materials, and scalable production solutions. Contact Hoplok Leather today to start crafting products that stand out in style and substance.
FAQ
What materials are commonly used in handbag manufacturing?
Handbags typically use full‑grain or top‑grain leather for luxury lines, PU/PVC synthetics for affordability, nylon and canvas for durability, and eco‑friendly options like recycled PET or plant‑based leathers to meet sustainability goals.
How long does it take to manufacture a handbag?
Prototype sampling takes 2–7 days. Small production batches (100–500 units) usually require 3–4 weeks, while larger runs (1,000+ units) can take 6–8 weeks, depending on complexity, material availability, and factory capacity.
What is the difference between handcrafted and machine‑made handbags?
Handcrafted handbags feature artisanal stitching, hand‑finished edges, and bespoke details, ideal for luxury markets. Machine‑made bags use automated stitching and hardware presses, offering consistency, higher output, and lower per‑unit costs for mass‑market production.
How do manufacturers ensure handbag quality?
Quality is enforced through multi‑stage inspections: incoming material checks, inline stitch and hardware audits, and final durability tests (zipper pulls, seam strength, load‑bearing). Compliance with ISO9001 and LWG ensures consistent standards and ethical practices.
What role does sustainability play in handbag production?
Sustainability drives material choices—recycled fabrics, eco‑tanned leathers, and plant‑based alternatives. Waste reduction techniques, renewable energy use, and ethical labor practices not only lower environmental impact but also meet growing consumer demand for responsible brands.
How can I start my own handbag product line?
Begin with concept sketches and market research, create detailed tech packs, and partner with a reliable manufacturer like Hoplok Leather for prototyping. Scale through small initial MOQs, refine designs, then expand production as demand grows.